 Previous Page Next Page
Previous Page Next Page
For a query built on tables, views, and synonyms from one JDBC connection only, its SQL statements can be edited.
To edit the SQL statements of a query, in the Query Editor click Menu > View > Edit SQL, the SQL dialog is then displayed showing the SQL statements used to execute the query like below.
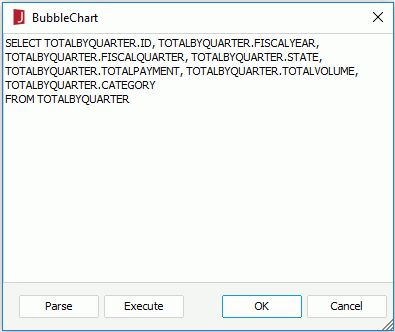
You can edit the query statements in the text area as follows:
Notes:
When creating a query using the Query Editor, JReport allows you to copy and paste your own SQL statements directly in the SQL dialog as explained above. However, because JReport query parser recognizes a limited set of the SQL 92 standard, sometimes JReport is not able to parse the customized SQL statements. For example, functions such as aggregations using the GROUP BY clause are not supported. In this case, a warning message is displayed after you click the OK button in the SQL dialog asking whether to continue using the customized SQL statements. If you choose Yes, the customized SQL mode is enabled, in which all the functions in the Query Editor will be disabled, and you can only edit the query by modifying the SQL statements in the SQL dialog. You should guarantee the correctness of the customized SQL statements since JReport will not parse it although you can check it by using Execute and passing it to the database to check.
While using the customized SQL mode, you can see that the Menu > Query > Customized SQL Mode option of the Query Editor is enabled and checked. By unchecking this option, you can go back to use functions of the Query Editor, in which case the customized SQL statements will be lost and the SQL statements generated by JReport will be applied instead.
Therefore, if you want to use customized SQL, it is much better to copy your SQL to a text file and import it using the Import SQL feature.