 Previous Page Next Page
Previous Page Next Page
You have two ways to add an HDS to a catalog:
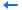
If you want to add the HDS to a new data source in the catalog, select any of the existing catalog data source, click New Data Source on the Catalog Manager toolbar, then in the New Data source dialog, specify the name of the data source, select the Hierarchical connection type and click OK.
If you want to add the HDS to a new data source in the catalog, select any of the existing catalog data source, click New Data Source on the Catalog Manager toolbar, then in the New Data source dialog, specify the name of the data source, select the XML connection type, check the Hierarchical Data Source radio button and click OK.

The following examples explain the above two methods in detail.
There are three classes used in this example. Their source code files are HierarchicalDataSource.java, HierarchicalDatasetMetaData.java, and HierarchicalDataset.java, which are available in <install_root>\help\samples\APIUDS\hierarchicalUDS. In this example, the HierarchicalDataSource.java will return the result set from the demo HSQL DB.
<install_root>\help. Modify the demo HSQL DB path in both HierarchicalDatasetMetaData.java and HierarchicalDataset.java.<install_root>\help into the ADDCLASSPATH variable of the batch file setenv.bat in <install_root>\bin, so that at runtime HierarchicalDataSource can be found.To import an HDS from an XML file, follow the steps below:
<install_root>\Demo\Reports\SampleReports.JReport Designer supports all kinds of URI as the XML data source.
http://localhost:8888/jrserver%2fSampleReports%2fSampleReports.cat/Key Performance Indicators Report.cls?jrs.cmd=jrs.try_vw&jrs.result_type=7&jrs.param$p_Year=2016&jrs.param$p_Month=2&jrs.param$p_Region=APAC
It is the URL used to run the sample report Key Performance Indicators Report.cls to the XML format in JReport Server. Type the URL into the XML URI text field, and click the Load Tree button, the structure of the returned XML stream will be loaded in the Structure box (before doing so, make sure that JReport Server is started). Modify the column properties in the Columns box as required.
The colon ':' and '@' symbols are used to identify JReport parameter names. If these symbols are used in your XML URI and you do not want JReport to parse them as parameters, you must add quotation marks to them. For example, when you browse to d:\test\employee.xml, you can quote it either as "d:\test\employee.xml" or d":"\test\employee.xml.
Note that you should check the No Security Checking option on the JReport Server Administration > Configuration > Advanced page before parsing this URL. In addition, JReport parameters can be dynamically referenced in the URI for setting different values at runtime.
When importing the XML file, you have to define the types of some data in the Format column. For example, if it is Date type, such as 1978-03-12, in the corresponding Format column, type in yyyy-MM-dd. If the data is $12,345.32, in the corresponding Format column, type in $##,###.##. By default, the value of the Scale column is 0, therefore, for decimal type data, you will have to specify the scale value in its corresponding Scale column, that is, modify this value to the number of digits that you want to appear to the right of the decimal point, for example, if the data is 123.23, then in the Scale column, modify this value to 2. For the Currency and Array columns, check them if required.
When you import an XML format HDS with an XSD file, the XML file only provides the data to the JReport Designer reports, while the structure, data type, and so on of the data from the XML file is defined in the XSD file. That is, the structure of the HDS is determined by the XSD file. You should be aware of the following points about the XSD file in order to generate a correct report based on an XML format HDS with an XSD file.
Data type conversion table
Before the data type defined in the XSD file can function with JReport Designer, it should first be converted into a corresponding data type when the XML format hierarchical data source is imported, following the rules in the conversion table below.
| XML Data Type | JReport Data Type |
|---|---|
| SchemaSymbols.ATTVAL_BOOLEAN | java.sql.Types.BIT |
| SchemaSymbols.ATTVAL_INT | java.sql.Types.INTEGER |
| SchemaSymbols.ATTVAL_SHORT | java.sql.Types.SMALLINT |
| SchemaSymbols.ATTVAL_BYTE | java.sql.Types.TINYINT |
| SchemaSymbols.ATTVAL_INTEGER | java.sql.Types.INTEGER |
| SchemaSymbols.ATTVAL_NONPOSITIVEINTEGER | java.sql.Types.INTEGER |
| SchemaSymbols.ATTVAL_NEGATIVEINTEGER | java.sql.Types.INTEGER |
| SchemaSymbols.ATTVAL_NONNEGATIVEINTEGER | java.sql.Types.INTEGER |
| SchemaSymbols.ATTVAL_UNSIGNEDLONG | java.sql.Types.BIGINT |
| SchemaSymbols.ATTVAL_LONG | java.sql.Types.BIGINT |
| SchemaSymbols.ATTVAL_UNSIGNEDINT, //4294967295 | java.sql.Types.BIGINT |
| SchemaSymbols.ATTVAL_UNSIGNEDSHORT, //65535 | java.sql.Types.INTEGER |
| SchemaSymbols.ATTVAL_UNSIGNEDBYTE, //255 | java.sql.Types.SMALLINT |
| SchemaSymbols.ATTVAL_POSITIVEINTEGER | java.sql.Types.INTEGER |
| SchemaSymbols.ATTVAL_FLOAT | java.sql.Types.FLOAT |
| SchemaSymbols.ATTVAL_DOUBLE | java.sql.Types.DOUBLE |
| SchemaSymbols.ATTVAL_DECIMAL | java.sql.Types.DECIMAL |
| SchemaSymbols.ATTVAL_STRING | java.sql.Types.VARCHAR |
| SchemaSymbols.ATTVAL_DATE | java.sql.Types.DATE |
| SchemaSymbols.ATTVAL_TIME | java.sql.Types.TIME |
| SchemaSymbols.ATTVAL_DATETIME | java.sql.Types.TIMESTAMP |
| SchemaSymbols.ATTVAL_HEXBINARY | java.sql.Types.LONGVARBINARY |
Note:
XSD structure supported by JReport Designer
In JReport Designer, not all XSD structures can be supported. The following diagrams show which structures are supported by JReport Designer.
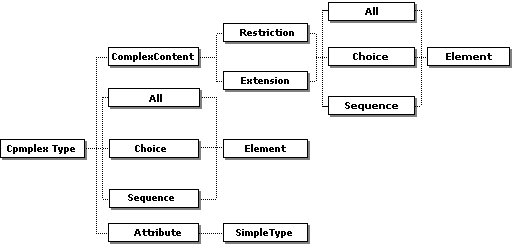
The Element type in the diagram can be of simpleType, ref, or complexType (it is different from the ComplexType in the root of this diagram. It can be global complexType but cannot be the anonymous one. If you have defined a complexType named A, and in this complexType A redefined an element as complexType named B, then the elements belong to complexType B must be of the simpleType).
The Attribute type in the diagram should be of the anonymous type or of the schema built-in type, such as xs:string.
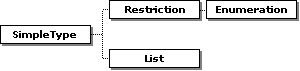
SimpleType here should be of the schema built-in type, such as xs:string. List type here cannot support some functions, such as minLength, and maxLength.
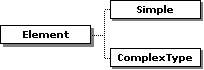
ComplexType here can include both global and anonymous complexType. The anonymous type means you do not give a name to the type, for example:
|
From the code above, you can see that the simpleType in the element aa has no name specified.
Notes: