 Previous Page Next Page
Previous Page Next Page
A business view contains database connections and relationships between view elements. It shields report end users from having to understand the physical structure of a data source, and enables them to build reports and analyze data based on a set of view elements they can understand. It also enables IT professionals to maintain control of the business data and ensure its integrity, while presenting end users with an intuitive view of the underlying data structures.
To make use of business views at server runtime, they need to be defined in JReport Designer in advance and then published to JReport Server. For additional information, see Business Views in the JReport Designer User's Guide.
A business view may contain category objects and the following view elements: group objects, aggregation objects and detail objects.
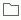 indicates that an object is a category. Categories are only for categorizing view elements, and they cannot be inserted into a report. The category is often used for indicating the name of the underlying DBMS table.
indicates that an object is a category. Categories are only for categorizing view elements, and they cannot be inserted into a report. The category is often used for indicating the name of the underlying DBMS table.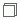 indicates that an object is a group object. A group object can be inserted as a column or row field in a crosstab, or as a group field or detail field in a table, or displayed as category/series field in a chart.
indicates that an object is a group object. A group object can be inserted as a column or row field in a crosstab, or as a group field or detail field in a table, or displayed as category/series field in a chart.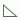 indicates that an object is an aggregation object. An aggregation object can be inserted into the group header or footer in a table, or into a crosstab as an aggregate field. An aggregation object can also be used as a detail field in a table although it will display the same aggregate value for every detail line. Web Report Studio will calculate the summary values based on the group level the aggregation object has been inserted into. An aggregation object is the only object that can provide the value on a chart.
indicates that an object is an aggregation object. An aggregation object can be inserted into the group header or footer in a table, or into a crosstab as an aggregate field. An aggregation object can also be used as a detail field in a table although it will display the same aggregate value for every detail line. Web Report Studio will calculate the summary values based on the group level the aggregation object has been inserted into. An aggregation object is the only object that can provide the value on a chart. 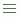 indicates that an object is a detail object. A detail object can be inserted into a table as a detail field. Detail objects cannot be used in charts and crosstabs.
indicates that an object is a detail object. A detail object can be inserted into a table as a detail field. Detail objects cannot be used in charts and crosstabs.