 Previous Page Next Page
Previous Page Next Page
Using a Query to Filter Multiple Queries
The Data Source Filter property is added to queries for specifying whether or not a query works as a data source filter. By setting a query's Data Source Filter property to true and joining the query with other data resources, the filters defined in the query will be applied to all the other queries in the same catalog data source when the following conditions are satisfied:
- The queries contain the data resources with which the data source filter query is joined.
- The queries do not contain any of the data resources that are included in the data source filter query.
To create a query and use it as a data source filter:
- Create the query with the required data resources.
- Create filters on the query, then save the query.
- In the Catalog Manager, click Pre-join.
- In the Select Data Source dialog, select the catalog data source in which the query is created and click OK.
- In the Pre-join Editor, click Add Tables.
- In the Add Tables/Views/Queries dialog, select the query you just created and the data resources which you want to join with the query, then click OK.
- Define the joins between the query with the other data resources and save them. For more information, see
Defining the join relationships between tables.
- Set the Data Source Filter property of the query to true.
Tip: By default, the properties in the Catalog Manager cannot be edited. To make the properties editable, click Options on the Catalog Manager toolbar. In the Options dialog, select Catalog in the Category box, then uncheck the option Forbid editing data object properties and click OK to confirm the change.
The following example shows the usage of data source filter in detail. In this example, we add a filter Order ID > 3400 on a query and make it work as a data source filter. The example is based on the SampleReports catalog in <install_root>\Demo\Reports\SampleReports.
- In the Catalog Manager, right-click the Queries node in Data Source 1 and select New Query from the shortcut menu.
- In the Enter Query Name dialog, input DSFQuery and click OK.
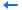
- In the Add Tables/Views/Queries dialog, expand the JDBC connection > Tables node, select Orders, click
 to add it to the right box, then click OK.
to add it to the right box, then click OK.
- In the Query Editor, select all the columns in the Orders table by selecting the top checkbox.
- Click Menu > Query > Filter.
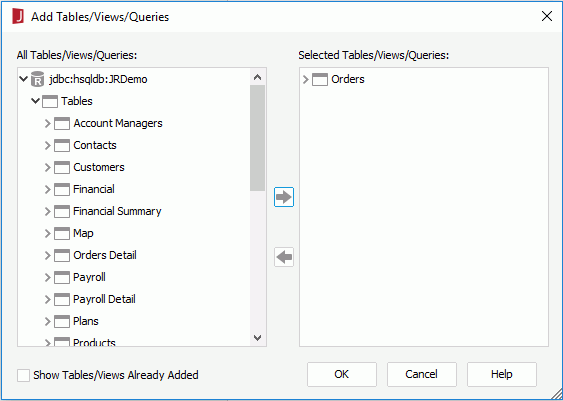
- In the Search Condition dialog, click Add Condition to add a line, define the filter as @ORDERID > 3400, and then click OK.
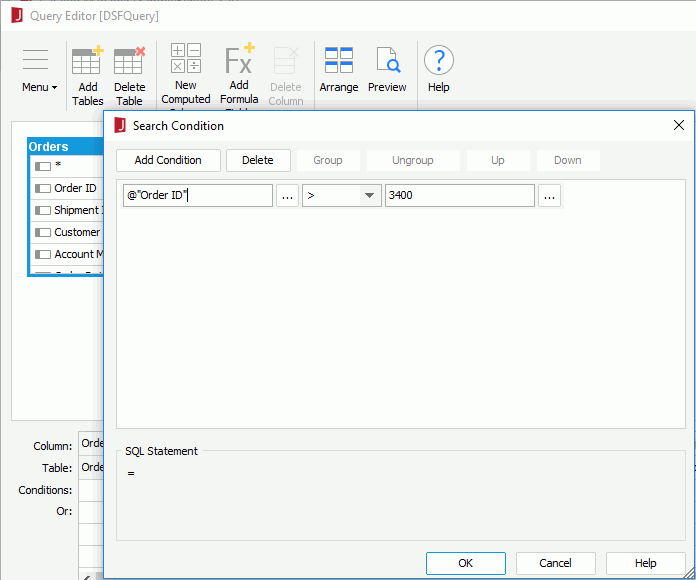
- Click OK in the Query Editor. The query DSFQuery is now added under the Queries node in the Catalog Manager and selected by default.
- In the Catalog Manager, click Show Properties, then set the query's Data Source Filter property to true.
Next, we will create a pre-join to join DSFQuery with the table Orders Detail.
- Click Pre-join on the Catalog Manager toolbar.
- In the Select Data Source dialog, select Data Source 1 and click OK.
- In the Pre-join Editor, click Add Tables.
- In the Add Tables/Views/Queries dialog, add the table Orders Detail and the query DSFQuery, then click OK.
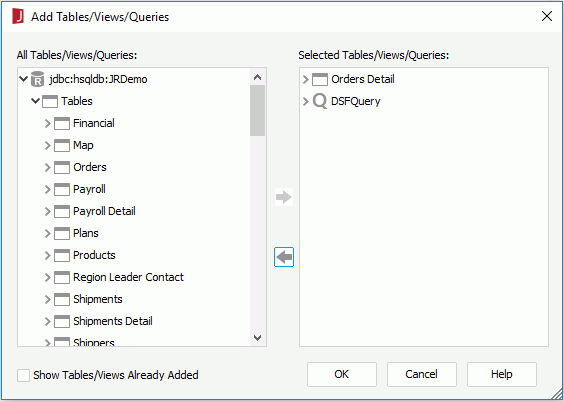
- Join DSFQuery and Orders Detail by connecting the Order ID columns.
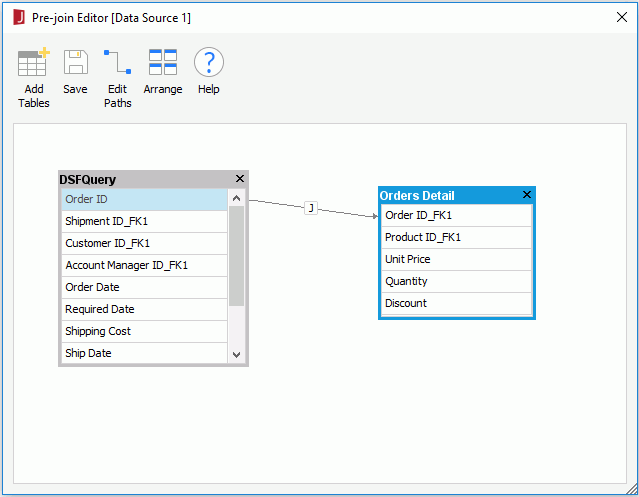
- Click Save to save the pre-join. Click Yes in the message dialog to accept the default path.
Next, we will create another query that contains the table joined with DSFQuery and use the query to create a report to test the data source filter.
- Repeat steps 1 to 4 to create another query named OrdersDetail which contains the Orders Detail table with all of its columns.
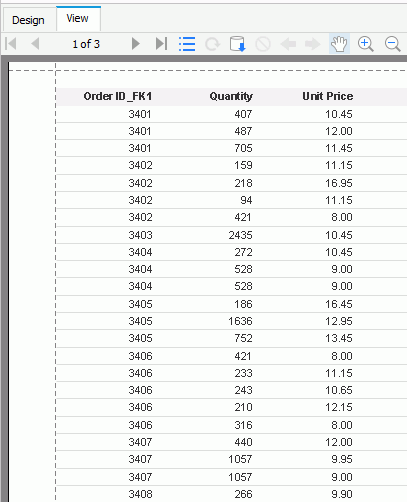
- Create a page report with a standard banded object in it based on the OrdersDetail query, which displays the fields Order_ID_FK1, Quantity and Unit Price.
- Preview the report. We can see that only the records the order IDs of which are higher than 3400 are shown.
 Previous Page Next Page
Previous Page Next Page
 Previous Page Next Page
Previous Page Next Page
 to add it to the right box, then click OK.
to add it to the right box, then click OK.




