 Previous Page Next Page
Previous Page Next Page
When you create data components in a report, datasets are created. A dataset is the set of data built from the result of a query, stored procedure, imported SQL, UDS, HDS or business view, and can optionally have filters applied to it. A dataset built on data resource such as query, stored procedure, imported SQL, UDS, and HDS contains all the DBFields in the data resource, as well as parameters and valid formulas in the catalog data source where the data resource is added; a dataset created from a business view contains only view elements and dynamic resources.
A dataset has a name, which by default is the name of the resource on which it is created. For a page report that is created using query resources, you can view items in a dataset by choosing the Dataset View mode from the toolbar of the Data panel.
Datasets in a page report can be shared by different data components. Having data components in the same page report use an existing dataset whenever possible will have a dramatic effect on the performance of your reports in the runtime environment. This is because each dataset is created by running a query against the database, and that is the most expensive part of running a report in terms of execution time. Even when two datasets are based on the same query JReport will still run the query separately for each dataset.
To create a dataset, take any of the following ways:
When you create a data component using the report wizard, a dataset is created at the same time, either empty or containing some data fields, depending on whether data fields are added to the data component.
Note: If a dataset is created on a hierarchical data source, when you use the dataset to create data components, pay attention to the unique features of HDS.
After you have created datasets in a report, you can manage them using the Manage Datasets dialog, for example, you can filter the datasets. To display the dialog, click Report > Manage Datasets.
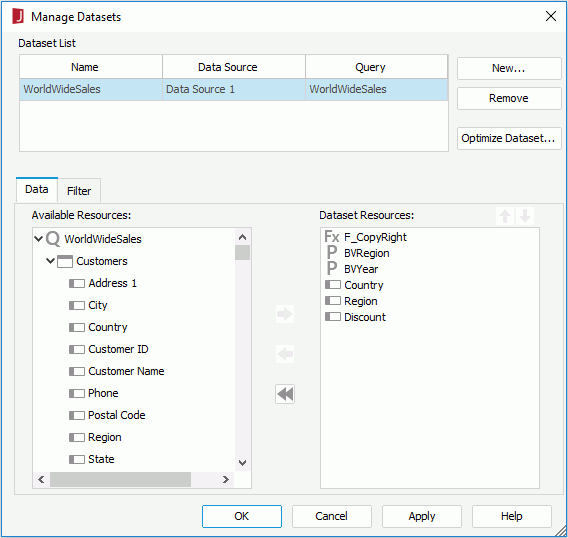
For any dataset, JReport automatically adds fields to it when fields are added to the data components that use the dataset, and removes the fields from the dataset once you remove them from the data components that use it. So there generally is no need to ever add or remove fields from a dataset specifically. However, in the Manage Datasets dialog, you can still manually add or remove data fields from a dataset.
 to add them to the dataset. You can also select a field and drag and drop it into the Dataset box.
to add them to the dataset. You can also select a field and drag and drop it into the Dataset box.  . Only the fields which are not used by any data component created on the dataset, either directly or indirectly, can be removed. To remove all the data fields in a dataset, click
. Only the fields which are not used by any data component created on the dataset, either directly or indirectly, can be removed. To remove all the data fields in a dataset, click  , however, when you click the button, only the unused data fields will actually be removed. When you enter the dialog the next time, you will find that the data fields used by data components created on the dataset will still display in the Dataset box.
, however, when you click the button, only the unused data fields will actually be removed. When you enter the dialog the next time, you will find that the data fields used by data components created on the dataset will still display in the Dataset box. and
and  to adjust the order of the added fields in the Dataset box.
to adjust the order of the added fields in the Dataset box. For a dataset created on a query, stored procedure, imported SQL, UDS, or HDS, you can filter on any DBField in the data resource, or a parameter or valid formula that is in the same catalog data source as the data resource. For a dataset created on a business view, you can only filter on a group or detail object in the business view.
 to specify the value of how to filter the field in the displayed dialog or input the value manually. You can use a DBField or a formula as the value to filter the dataset, or the special field User Name or a parameter to filter the dataset dynamically (for the usage of parameters in filter conditions, see the example in Dynamically Filtering Queries).
to specify the value of how to filter the field in the displayed dialog or input the value manually. You can use a DBField or a formula as the value to filter the dataset, or the special field User Name or a parameter to filter the dataset dynamically (for the usage of parameters in filter conditions, see the example in Dynamically Filtering Queries).
When you type in the value, if multiple values are required, they should be separated with ",", and if "," or "\" is contained in the values, write it as "\," or "\\".
To group some condition lines, select them and click the Group button, then the selected condition lines will be added in one group and work as one line of filter expression. Conditions and groups together can be further grouped. To take any condition or group in a group out, select it and click Ungroup.
To adjust the priority of the condition lines, select it and click the Up or Down button.
To delete a condition line, select it and click the Delete button.
Tips:
 on the toolbar of the Data panel.
on the toolbar of the Data panel.Note: The following SQL type of data cannot be filtered: Db.SQL_BINARY, Db.SQL_BLOB, Db.SQL_CLOB, Db.SQL_LONGVARCHAR, Db.SQL_LONGVARBINARY, Db.SQL_VARBINARY and Db.SQL_OTHER.
You can enlarge or decrease the scope of retrieved data for a dataset, and therefore make a balanceable decision between better performance and special usage cases/demands. However, this feature is not supported on datasets created from business views so only works for page reports that are created using query resources. For datasets created on business views, you can make use of the Prefetch property on the business views.
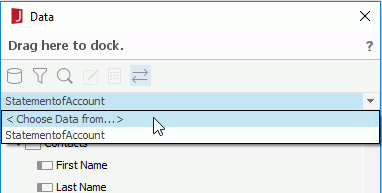
You can create datasets for a page report via the Manage Datasets dialog. To do this:
However, you should not rename a dataset that has been used by any data component. Renaming a referenced dataset will cause data components based on the dataset not to work.
However, if you remove a dataset directly in this way, any data components created based on the dataset will not work. So, when you want to remove a dataset, it is recommended that you first remove the data components which reference this dataset.