 Previous Page Next Page
Previous Page Next Page
Filter controls are used to filter one or more data components in a report or library component. They can do filtering based on the fields in the data sources (query resources or business views) the data components are created from. After inserting filter controls, you can also insert a navigation control for undoing/redoing the value selection in the filter controls. For details about the usage of navigation control, see Using Navigation Control to Undo/Redo Value Selection in Filter Controls.
There are three types of filter controls: text list, single value slider, and range slider.
Text lists allow you to pick one or more random values from a list and are used with categorical or nominal variables. You can choose one or more values from anywhere in the list and there is no mean or median value calculation possible such as States and Countries.
Single value sliders allow you to select one single value from a list and suitable for displaying a few values like quarters.
Range sliders allow you to pick multiple sequential values from a list and are used for interval variables such as dates, times, quantity and currency variables where the slider represents the scale from lowest to highest value and the middle represents the median value.
Think about what you need and choose the proper filtering tool.
Both sliders and text lists have the same filtering mechanism.
Filtering based on one field is a common usage. Bind a field to a filter control, and then based on the field to filter the data of the components created from the same data source as the field.
You can also bind multiple fields to a filter control and the values of the fields will be displayed in the filter control. It functions similarly as you put each field in a separate filter control. The difference is that the fields and their values are hosted in one filter control instead of many. If there are same name values, they will be distinctive. The selection of a distinctive value will filter all the data components created using the data sources that contain the bound fields to which the value belongs. The usage suits for fields with a few values and you need only one filter control.
Another special usage is to filter components using different data sources. Choose a common field all the data sources contain and then bind a filter control with the common field in all the data sources, that is, select the common field under the nodes of all the data sources. The name of the fields do not need to be the same but the data returned needs to be similar.
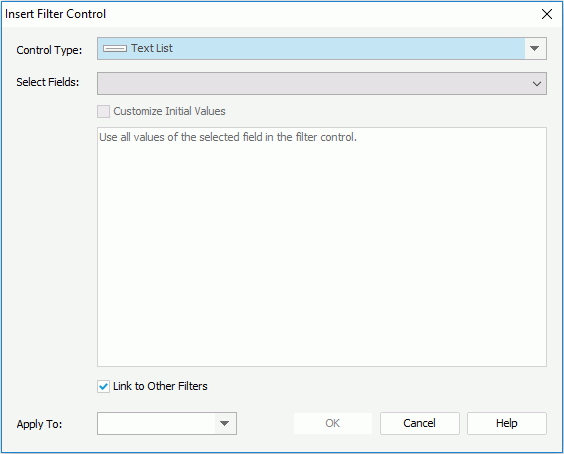
For example, there are two components containing data from different data sources, and you want to filter their data using one filter control. The precondition is that both data sources have the field you want to filter. For example, you would like the two components to show the data of a specific country. In order to do this, insert a filter control into the report, then select both the country fields from the two data sources (different data sources may use different names for the country field, for example, data source 1 uses "Country", data source 2 uses "P_Country", in this case, you need to select both "Country" and "P_Country"), then from the Apply To drop-down list, select the two components you want to filter, and then click OK. The filter control will be inserted in the report, and you can see it lists country names which come from the two data sources. In the filter control select one or more countries, then the two target components will be filtered and only display the data of these selected countries.
When you bind a filter control with multiple different fields, be sure the list of values in each field match so that when you select a value, such as Country, P_Country and S_Country, it will match the appropriate country field in each data source. The logic is the values are OR that is Field1=SelectedValue1 or Field2=SelectedValue1 or Field3=SelectedValue1. Therefore, when Field1, Field2 and Field3 are used in different components you will see the records correctly in each component.
When you bind a filter control with multiple different fields which do not contain the same list of values such as Country, Region and Territory, at runtime after you select values in the filter control, the filter condition will use OR logic to apply the selected values to all the fields of the filter control, for example, Field1=SelectedValue1 or Field2=SelectedValue1 or Field3=SelectedValue1. In this case, when there are three fields but the list of values in each field do not match, the result will have no matching records for two of the components and therefore become blank components. We recommend that you use three different filter controls in cases like this.
To insert a text list filter control into a report or a library component:
 from the Components panel to the destination.
from the Components panel to the destination.The Insert Filter Control dialog appears.
 button.
button.
In the text box, input one value in one row, and then press the Enter key to start a new row. General text editing operations including copy, paste, cut, backspace, delete and etc. are supported. You need to make sure the accuracy of the formats and values.
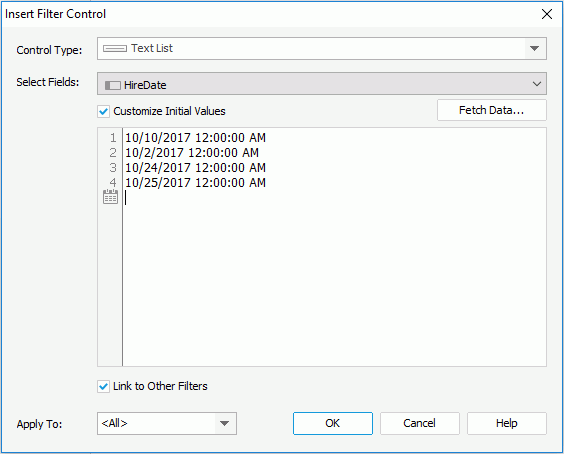
By default, JReport applies the filter to all the data components created using the data sources (query resources or business views) in which the selected fields are obtained. If you uncheck the data components which are based on the same data source as any selected fields, these fields will not be used in the filter and thus their values will not be listed in the filter control.
When done, click OK to insert the filter control. Then at runtime, values of the selected fields which are applicable to the specified data components will be listed in the filter control. End users can select one or more values to apply.
To insert a single value slider to a library component:
 from the Components panel to the destination. Then the Insert Filter Control dialog appears.
from the Components panel to the destination. Then the Insert Filter Control dialog appears.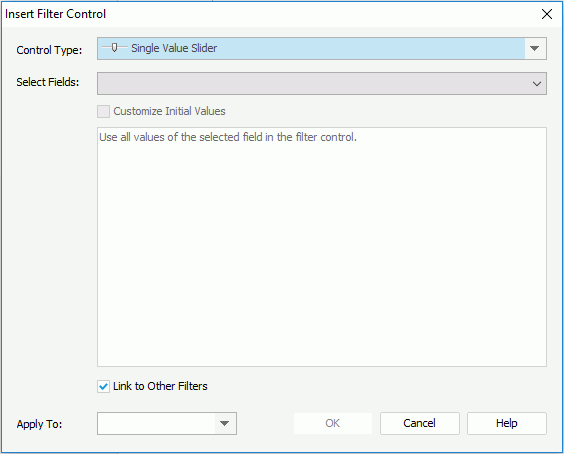

In the text box, input one value in one row, and then press the Enter key to start a new row. General text editing operations including copy, paste, cut, backspace, delete and etc. are supported. You need to make sure the accuracy of the formats and values.
For fields of Date/Time type, you can also specify a value using the  button and specify a special function.
button and specify a special function.
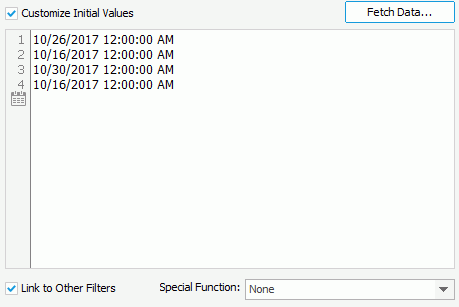
By default, JReport applies the filter to all the data components created using the business views in which the selected fields are obtained. If you uncheck the data components which are based on the same business view as any selected fields, these fields will not be used in the filter and thus their values will not be listed in the slider.
To insert a range slider to a library component:
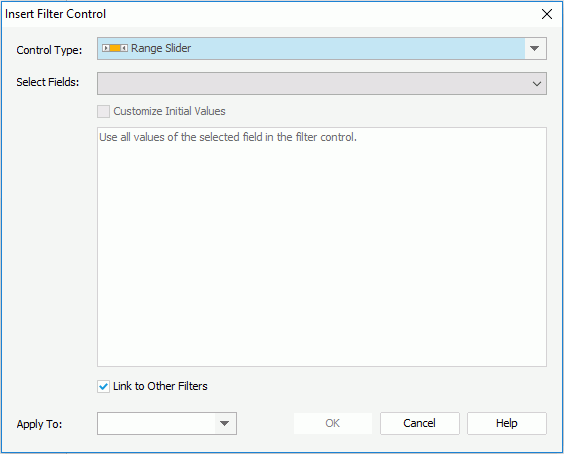

 button and specify a special function.
button and specify a special function.
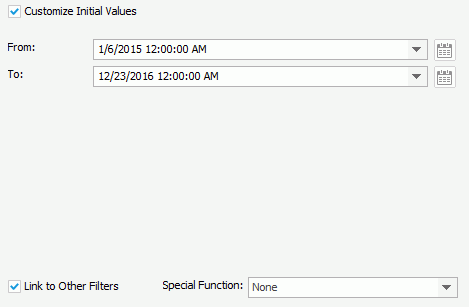
By default, JReport applies the filter to all the data components created using the business views in which the selected fields are obtained. If you uncheck the data components which are based on the same business view as any selected fields, these fields will not be used in the filter and thus their values will not be listed in the slider.
You can further modify the filter controls inserted into a report if you want.
To edit a filter control, right-click the filter control and select Edit Filter Control from the shortcut menu. In the Edit Filter Control dialog, edit the filter control settings.
Note: If all the data components in a report or library component that use a business view or query resource are deleted, the fields in the business view or query resource that have been added in the filter controls in the report or library component will be removed from the filter controls too.